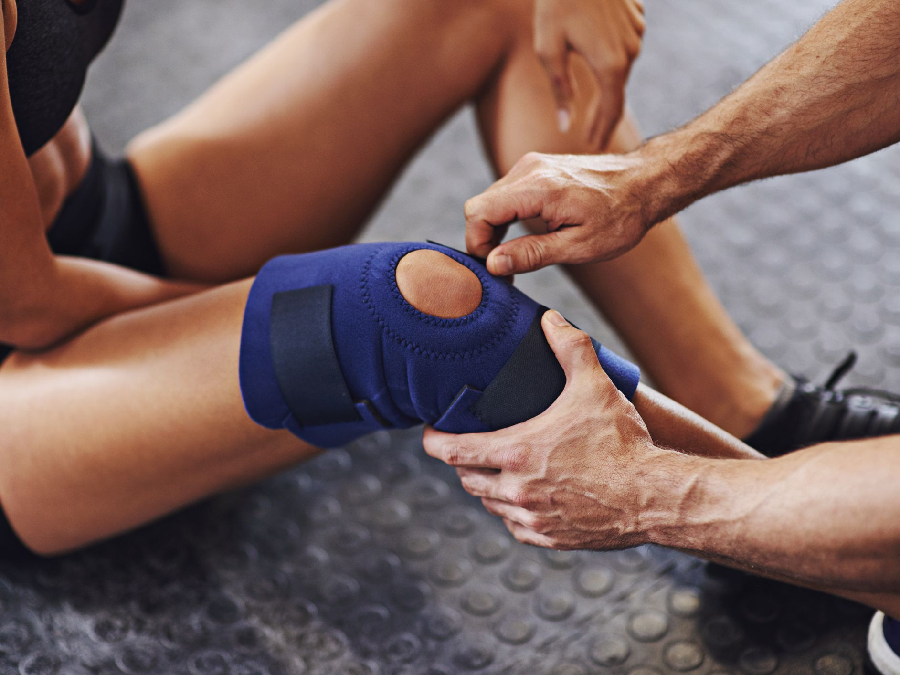
Sports medicine Meeker, Colorado treats a wide range of physical conditions, including acute trauma like fractures, sprains, strains, and dislocations. In addition, they treat chronic overuse injuries such as tendonitis, degenerative diseases, and overtraining syndrome. They combine general medical education with sports science, exercise physiology, orthopedics, biomechanics, sports nutrition, and sports psychology principles. A sports medicine team may include physicians, surgeons, athletic trainers, sports psychologists, physical therapists, nutritionists, coaches, and personal trainers, among others.
Sports medicine, also known as sports and exercise medicine (SEM), is a branch of medicine that focuses on physical fitness as well as the treatment and prevention of sports and exercise-related injuries. The goal of sports medicine is to assist people in engaging in an exercise in a safe and effective manner in order to achieve their training objectives.
Specialists of sports medicine Meeker, Colorado focus on the medical, therapeutic, and functional aspects of exercise, as well as working directly with athletes to improve their overall sports performance. The title “sports medicine specialist” does not always imply that the specialist is a doctor. It can be applied to any number of disciplines where sports medicine is used. It is not, in and of itself, a medical specialty. Rather, it denotes additional training focused on the medical aspects of sports.
Also, physicians in sports medicine Meeker, Colorado also specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of sports-related and exercise-related injuries and illnesses. While many sports medicine doctors only work with athletes, the vast majority will treat anyone who has sustained a sports injury. Before beginning a two-year fellowship in sports medicine, most sports medicine physicians are board-certified in family practice, emergency medicine, pediatrics, internal medicine, or orthopedics. Many will receive a Certificate of Added Qualifications (CAQ) in Sports Medicine from the American Board of Family Medicine upon completion.
Most sports medicine physicians deal with non-operative musculoskeletal conditions. Others are orthopedic surgeons who have decided to focus their practice on the surgical treatment of sports injuries. Beyond muscle, bone, and joint injuries, a sports medicine physician will be qualified to treat any number of other associated conditions, including concussion and other head injuries; chronic or acute illnesses (such as asthma, diabetes, or hypertension); Nutrition, supplements, ergogenic aids, and performance issues